Estimated Reading Time: 11 minutes
Over the past several years, there’s been a significant increase in mobile phishing attacks—particularly targeting enterprises. Lookout—a zvelo partner specializing in mobile security, particularly mobile phishing protection—reported that mobile phishing attacks have been increasing at a staggering year-over-year rate of 85% since 2011. Additionally, Lookout revealed that over the same period of time, more than half (56%) of their mobile users received and tapped on a phishing URL via their mobile device. Luckily, these users were protected—the malicious link neutralized before a connection was made.
But, according to Security Week, with over 66% of emails first being opened on a mobile device such as a phone or tablet—unprotected emails are one of the most significant security threats facing us today.
A Brave New World of Targeted Mobile Phishing Tactics
The latest iterations of phishing campaigns and strategies have seen an increase in sophistication—taking spoofed emails, phony websites, and credential hacking to the next level. For example, with the widespread adoption of SSL Encryption—in large part thanks to Let’s Encrypt!—phishing sites have largely shifted to using security features to enhance the effectiveness of mobile phishing attacks. A report from APWG (see chart below) indicated that during the course of a single year (2017), the percentage of phishing sites using encryption rose from less than 5% (end of 2016) to nearly a third (31%).
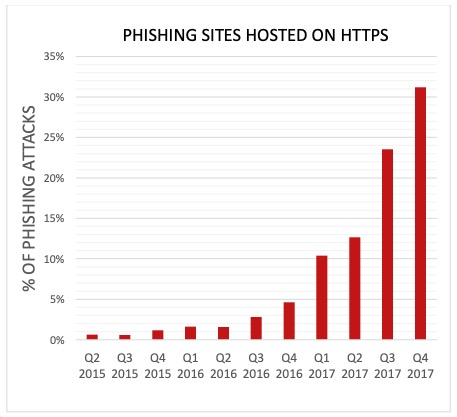
APWG Report – Phishing and SSL Adoption
The Modern Rogues recently shared that 1.5 million new phishing websites appear every single month, and the financial fallout from a successful corporate phishing attack chimes in to the tune of $1.6 million dollars annually for mid-sized companies. And that number is only growing.
No matter how diligently you and your team work to protect your organization against phishing attacks—new tactics, vectors, and threats are popping up every day. The top industry cybersecurity and antivirus companies agree that mobile phishing is one of the biggest and most frustrating unsolved problems in the enterprise today.
Why the Increase in Mobile Phishing Scams?
One of the primary reasons for the growth in mobile phishing attacks is due to the widespread proliferation of “smartphones”—used for work as well as in every aspect of our lives. Technology experts have spent decades building and bolstering cyber defenses for traditional network devices like laptops and computers—which have fairly static network connections and can be wholly managed by the company.
Enter the smartphone, a device that’s designed with a simplified UI for easy use in a small form factor and incredibly portable. We now have a device (or attack vector depending on how you see it) that’s always on, always connected, always with the user, and constantly connecting to a variety of networks—making it exceedingly difficult to protect and quarantine when compromised. It’s the perfect storm—giving bad actors a direct line to a growing body of vulnerable users.
It’s plain and simple—hackers are working overtime to take advantage and infiltrate devices and communications systems. Unfortunately, mobile devices are an ideal target for these attacks. Mobile devices are the perfect storm of ingredients—combining simplified user interface and design languages, always-on always-roaming devices constantly connecting to various networks, and the ideal personal notification device. Additionally, these devices also fall outside of the standard network security umbrella of protection.
In a study by the New York Post last year, it was found that the average American checks their phone nearly 80 times per day—or at least once every 12 minutes. We casually check our mobile device while waiting for the check at lunch, in line somewhere, before boarding a plane, etc.
The other reason is… they’re working. Today’s phishing tactics are both sinister and well executed. The first point of content for phishing attacks are generally via Email or SMS—prompting your organization’s busy and distracted mobile users to voluntarily offer up sensitive business or personal information. Some of the most common strategies include:
- Fake login forms mimicking business tools (G Suite, PayPal, Amazon, etc.)
- Malicious files and Trojans
- Personalized messages & social engineering
- Complex Mobile Advanced Persistent Threat (mAPT) phishing plots
- Link shorteners (pointing to malicious/phishing sources)
While IT teams are continuously learning and combating these threats—chances are the majority of users aren’t actively aware of threats or properly trained.
Do Traditional Approaches to Fighting Phishing Attacks for Fixed Devices Work as Effectively for Mobile Devices?
IT teams have fought phishing attacks on their organizations’ laptops and desktops for decades now, with varying degrees of success. Most success, however, comes down to a combination of the right tools, proper network management and oversight, and employee training. While some of the tools are different for mobile devices, the same overall approach and methodology applies.
 The dangers, however, are greater due to the mixed usage of BYOD mobile devices. Mobile usage in a corporate environment has blurred the lines of security—and hackers have recognized this—automatically putting smartphones at a greater risk for phishing schemes. Employees use the same phone to access business emails, files and related websites that they use to text, download personal apps, check social media accounts, stream music and movies, play games, and generally manage their day-to-day lives. All of this on a device format and screen size that has driven user experience and layout optimizations that ultimately omit and simplify data/tools to support a smaller screen size and format.
The dangers, however, are greater due to the mixed usage of BYOD mobile devices. Mobile usage in a corporate environment has blurred the lines of security—and hackers have recognized this—automatically putting smartphones at a greater risk for phishing schemes. Employees use the same phone to access business emails, files and related websites that they use to text, download personal apps, check social media accounts, stream music and movies, play games, and generally manage their day-to-day lives. All of this on a device format and screen size that has driven user experience and layout optimizations that ultimately omit and simplify data/tools to support a smaller screen size and format.
Lookout reminds us that traditional tools like firewalls, secure email gateways, and endpoint antivirus have been increasingly effective for laptops and desktops—but mobile devices inherently introduce new security risks, vulnerabilities, and challenges. The great news is that there are highly effective tools, strategies, and technologies—like URL categorization, malicious and phishing website detection, and web filtering—to help keep your organization’s mobile users vigilant when it comes detecting and avoiding mobile phishing ploys.
9 Tips to Improve Security Against Mobile Phishing Attacks
Our team understands the challenges that so many of our partners face when it comes to staying current on the latest approaches to effectively thwart and protect their end users from phishing attacks. From our work in malicious detection and URL categorization and conversations with partners—we’ve compiled these 9 high-level tips and practices that you can incorporate into your current strategy to improve mobile security and threat intelligence.
9. Enlist C-Level Support to Source Mobile Security Awareness
Maintaining mobile security is going to take some serious organizational resources, so make sure your C-level executives are fully on board. CSO recommends highlighting how heightened mobile security awareness to prevent phishing attacks will save your organization, time, money, human resources, and brand reputation. Buy-in from leaders will ensure your IT team has the resources and authority to implement effective policies and tools—as well as explore new options to increase security capabilities.
8. Create and Regularly Update Mobile Policies and Procedures
With your C-level support and respective department representatives aligned, the first thing to do is create or update policies and procedures to address mobile usage and foreseen security gaps. Make these a standard for training and onboarding with employees and make them readily available in hard copy and/or electronically.
A few basic policies and procedures sections you may wish to include are:
- Outline Approved Mobile Devices and Tech Support Availability
- Define On-Device Security Requirements (security features, apps, filtering, etc.)
- Determine Standard Network Access Practices for Mobile Devices
- Acceptable Uses/Behavior of Mobile Devices Associated with Your Organization
- Security Responsibilities to Avoid Negative Cyber-Events Like Phishing Attacks and Botnets
- Outline Best Practices such as Two Factor Authentication (2FA), Password Managers and encrypted file vaults, etc.
- Update Risks, Liabilities, and Disclaimers
7. Protect Against SMS and MMS Phishing Attacks
In mobile environments, phishing risks venture beyond traditional email tactics. Phishing attackers have found a variety of ways to exploit busy professionals’ reliance on texting and other communication apps. For similar reasons that professionals click on phishing URLs in emails; they may click on a dodgy link via SMS or MMS to experience a “SMiShing attack.”
Lifewire suggests a few simple tips to share with your team members to avoid getting SMiShed:
- Watch out for and avoid opening text messages coming from the number “5000”
- Do not reply to an unfamiliar or suspicious text without further investigation
- Use the cell phone provider’s Text Alias feature
- Enable “lock texts from the internet” if and when possible
These simple steps can help your team build safer habits and stay secure with mobile messaging features.
6. Detect and Block Email Spoofing with SPF Implementation
A Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an email validation tool that helps to eliminate email spam or spoofing by allowing you to list the mail servers that are permitted to send email on behalf of your domain. SPF indicates the source of a message then detects and prevents email spoofing with the gathered information regarding authenticity, per the Infosec Institute.
Setting up an SPF record with your email service is fairly straightforward and can help prevent your organization’s outgoing emails from being spoofed—or from being marked as spam.
5. Defend End-User Privacy with Compliance and Encryption
This tip is more of a preventative measure, but it is just as important to safeguard your network and data ahead of time. In the event a phishing attack does compromise your network—through a mobile device or a laptop/desktop—sensitive data will be protected.
Comply with any official policies and regulations regarding data collection, storage, transfer, and destruction to protect valuable customer, employee, and stakeholder information before it becomes the subject of a phishing attack.
Rely on your legal and compliance professionals, along with internal auditors to guarantee you abide by any regulations, policies, or standards set forth by any local, state, and federal body—as well as any requirements by related private organizations that govern your industry.
Another commonly employed end-user defense measure is to encrypt all sensitive company information to make sure that only designated recipients can read messages and data. A well secured network doesn’t have just one wall of defense. When you take steps to harden and secure your entire network and data—it makes it increasingly difficult for intruders to abscond with important information—even if they make it beyond the first wall.
4. Filter Spam Emails
Phishing attacks are often enveloped inside of those “friendly” email messages that ultimately end up cluttering spam folders around the world. We recommend that you regularly monitor and redirect spam emails—that way your employees don’t have to deal with them at all.
3. Reinforce Security Policies and Practices with Regular Employee Training Sessions
Once you have your policies, procedures, software and other tools in place, you need to make sure your staff is on board and ready to help you keep everything running smoothly with routine phishing awareness training.
A few fundamental training criteria that every employee must learn include:
- Keep software and operating systems patched and up to date to protect against the latest known security vulnerabilities.
- Installing and maintaining security apps, or seeking the assistance of an IT team member to do so.
- Never blindly allowing apps from unknown sources to access a mobile device’s features. These features include files, camera and photographs, geolocation and anything else that’s not solely related to your business’s purposes.
- Denying requests to provide login IDs and passwords by unknown sources.
- Activating tools to identify malicious websites that may lead to phishing attempts.
- Be wary of link shorteners and whenever in doubt use a tool like Unshorten.it (also available as a browser extension) to expand and analyze the URL before visiting.
2. Adopt Awareness Tools & Internal Testing
Procedures, policies, and training sessions are critical methods of building awareness among staff, management, and the executive team. You can gently, but consistently, reinforce how important it is to remain vigilant about the threats of mobile phishing in internal emails, newsletters, blog posts, and phishing simulations.
“Knowledge is half the battle.” – G.I. Joe
The most secure organizations in the world utilize “whitehat” hacking and penetration testing to continuously “pressure test” their defenses. Once you have the basics in place—you must continue to monitor and optimize, thus improving your systems to better protect your organization.
Which brings us to the #1 spot…
1. Identify Malicious & Phishing Website URLs and Block Connections
It’s almost a hard-and-fast industry rule for fixed device and mobile users alike. Always stay alert regarding any URLs included in emails—especially emails from unknown sources. Having a keyboard, mouse, and large display makes forensic analysis of URLs significantly easier—making it so important to have filtering and security apps in place on mobile devices to aid in malicious detection and prevention.
Hyperlink or URL masking can fool even the most astute and security-conscious. By concealing the true destination, or using homograph attacks (IDNs), bad actors can trick a growing percentage of mobile users in our fast-paced culture. When it comes to URLs and hyperlinks embedded in anchor text—the best advice we can give you is to adopt a zero trust mindset.
You can save time and frustration for your employees by investing in a premium web content filtering service that identifies malicious website URLs and helps block connections before reaching the requestor.
The following are a few features and characteristics you should look for when it comes to finding the right web filtering and malicious website detection tools and services:
- Real-time identification and updates for malicious URLs and IPs associated with phishing, fraud, spyware, malware, command and control, botnets, and other harmful programs.
- High coverage rate for ActiveWeb URLs and IPs. Websites are popping up and being retired everyday. The lifespan of malicious sources can vary significantly, and a filtering solution with a high coverage rate shows that it is actively monitored and managed to handle those changes.
- Accuracy of category values and safety status for ActiveWeb URLs and IPs. It’s not enough to just have high coverage—a best-in-class filtering solution has systems and processes in place to achieve unmatched accuracy—ensuring a limited number of false positives and the highest quality protection against malicious sources.
- Flexible, scalable, and redundant infrastructure. A best-in-class premium web filtering solution will offer flexible deployment options to meet the infrastructure demands of your organization. It will also be scalable and redundant, ensuring it can handle any spikes in traffic with little-to-no downtime.
Still Concerned About Phishing Attacks?
We are too! zvelo partners with some of the world’s leading antivirus vendors, ISPs, Telcos, and device manufacturers who leverage the zveloDB™ URL Database and our real-time content categorization engine for phishing detection, malicious website detection, and cyber threat intelligence feeds to empower their web filtering & parental controls, and security solutions. If you’re interested in evaluating the zveloDB for your application in network security, ad tech, or mobile and subscriber analytics—don’t hesitate to contact us.





